What is Web Components ?
Web Components is a suite of different technologies allowing you to create reusable custom elements — with their functionality encapsulated away from the rest of your code — and utilize them in your web apps. (Source: MDN)
What make a Web component ?
- Custom Elements: The Custom Elements specification lays the foundation for designing and using new types of DOM elements.
- Shadow DOM: The shadow DOM specification defines how to use encapsulated style and markup in web components.
- ES Modules: The ES Modules specification defines the inclusion and reuse of JS documents in a standards based, modular, performant way.
- HTML Template: The HTML template element specification defines how to declare fragments of markup that go unused at page load, but can be instantiated later on at runtime.
Why Web components ?
As developers, we all know that reusing code as much as possible is a good idea. This has traditionally not been so easy for custom markup structures — think of the complex HTML (and associated style and script) you’ve sometimes had to write to render custom UI controls, and how using them multiple times can turn your page into a mess if you are not careful. ( MDN )
- Reusability
- Maintainability
- Productivity
- Composability
- Following web standards
Angular
Angular is a TypeScript-based open-source web application framework led by the Angular Team at Google and by a community of individuals and corporations.
The main building blocks are modules, components, templates, metadata, data binding, directives, services, and dependency injection (see figure below).

Angular component
Components are the main building block for Angular applications. It is a building block built on top of Web component. Each component consists of:
- An HTML template that declares what renders on the page
- A Typescript class that defines behavior
- A CSS selector that defines how the component is used in a template
- Optionally, CSS styles applied to the template
Please read the documentation here.
We build Web application in composing components. Each component could be instatiated using a custom tag (See figure below).
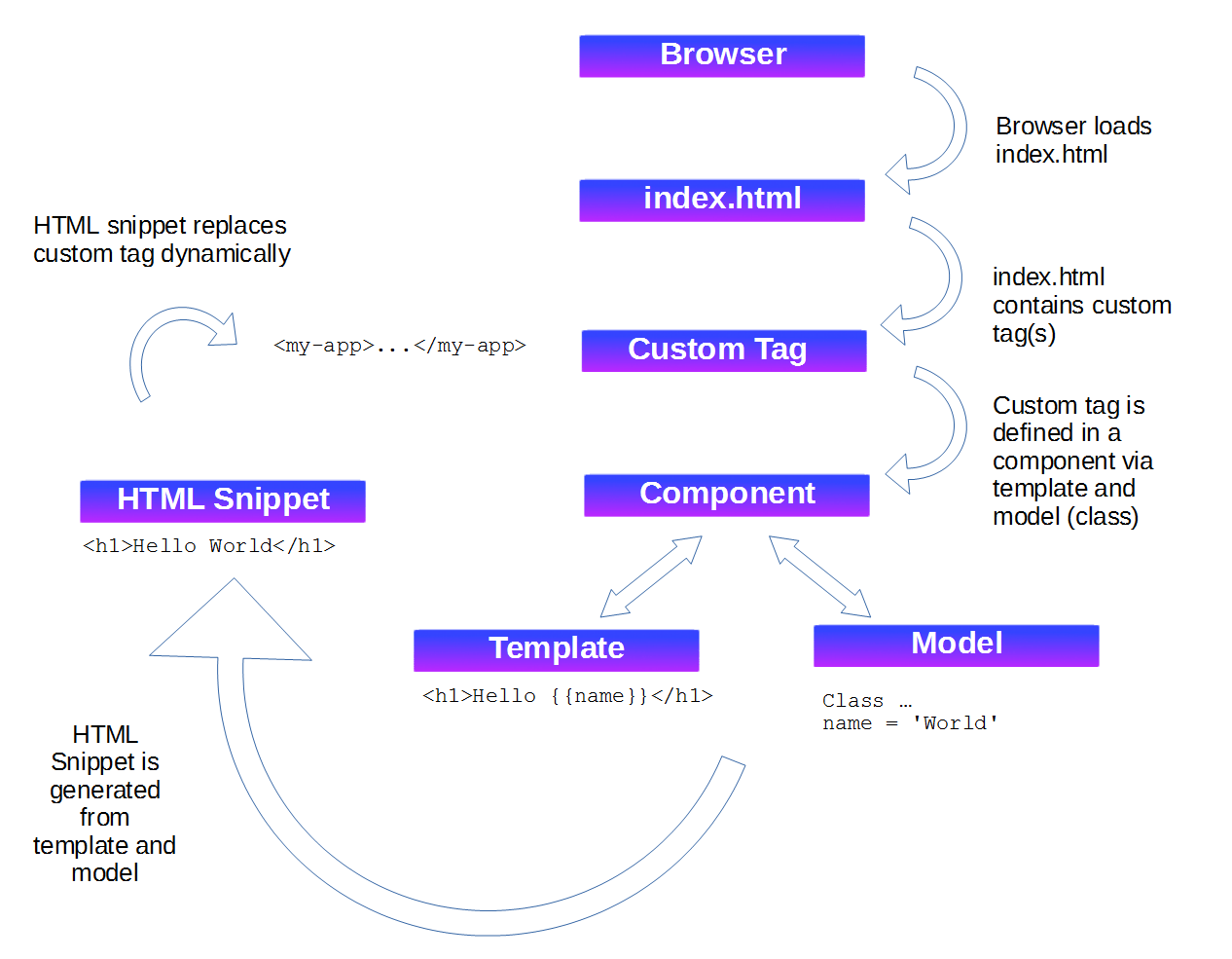
In the case of a simple component, the typescript class is empty because this component doe not have any dynamic behaviour.
import { Component, OnInit } from "@angular/core";
@Component({
selector: "my-app",
templateUrl: "./my-app.component.html"
})
export class MyAppComponent implements OnInit {
name = 'World';
constructor() {}
ngOnInit() {}
}The html template contains basic html element or custom tag to instantiate other components.
<h1>Hello {{name}}</h1>Among the cool feature of Angular, it manages
TypseScript
Currently angular projects are built with Typescript, as I already mentioned, is a superset of JavaScript which primarily provides optional static typing, classes and interfaces. One of the its salient benefits is to enable IDEs to provide a richer environment for spotting common errors as you type the code. Unlike CoffeeScript or Dart, TypeScript is not a stand-alone language.
This language ensures an improved refactoring, navigation, and auto-completion services. You can even opt out of its inbuilt features when needed.
Declarative UI
Angular uses HTML to define the UI of the application. HTML, as compared to JavaScript, is a less convoluted language. HTML is also a declarative and intuitive language. How will it help ? You don’t need to invest your time in program flows and deciding what loads first. Define what you require and Angular will do the job.

Angular Testing
In Angular, testing is extremely simple. Angular.js modules has the application parts that are easy to manipulate. With module separation, you can load the necessary services, while effectively performing automatic testing using Jasmine, Karma.. etc . You don’t even need to remember module loading order if you follow “one file-one module” principle.
Simplified MVC Pattern MVVM
Angular framework is embedded with original MVC but it’s more of an MVVM software architectural setup. Angular does not ask developers to split an application into different MVC components and build a code that could unite them. Its framework uses the MVVM(Model-View-ViewModel) architecture better than an MVC (Model-View-Controller) one. The MVVM model supports two-way data binding between View and ViewModel. This allows the automatic propagation to change within ViewModel’s state to the view. Typically, ViewModel uses the observer model to inform changes to the ViewModel model to model.

Furthermore, it only asks to divide the app and takes care of everything else. Therefore, Angular and MVVM (Model-View-View-Model) design structure are quite similar. Angular ensures easy development as it eliminates the need for unnecessary code. It has a simplified MVC architecture, which makes writing getters and setters needless. Directives can be managed by some other teams as these are not part of app code. All in all, developers are promised less coding along with lighter and faster apps. According to Amazon, every 100-millisecond improvement in page loading speed led to 1% increase in revenue.
Modular Structure
Angular organizes code into buckets, whether it is components, directives, pipes or services. Those who are familiar with Angular refer to these buckets as modules. Modules make application functionality organization easy through dividing it into features and reusable chunks. Modules also allow lazy loading, which paves way for application feature loading in the background or on-demand. Angular makes it an achievable goal to divide the labor across different team members while ensuring organized code. In fact, you can make the best modules when you have a proper understanding of it. Developers can improve productivity with appropriate modules built.
Code Consistency
Any code base requires consistent coding. A writer knows how important consistency is in their content. We know if the content fails to resonate with the readers to a deeper level at any touch-point, we are on a downward slope of lead conversions, and coding is no different. Inconsistent coding increases the risks of delayed launches or elevated costs. However, consistent coding has several benefits, such as making sites easier to use and enabling the use of templates or pre-defined code snippets. Angular framework is based on components, which begin in the same style. For instance, each component places the code in a component class or defines a @Component decorator (metadata). These components are small interface elements independent from each other, and thus, offer you several benefits, including:
- Reusability: The component-based structure of Angular makes the components highly reusable across the app. You can build the UI (User Interface) with moving parts, while also ensuring a smooth development process for developers.
- Simplified Unit-Testing: Being independent from each other, the components make unit testing much easier.
- Improved Readability: Consistency in coding makes reading the code very easy for amateur developers on an ongoing project, which adds to their productivity.
- Ease of Maintenance: Decoupled components are replaceable with better implementations. Simply put, it enables efficient code maintenance and update.
finally, I just advice you to learn Angular and try to build something out of it which will give you a better idea about how efficient using it.